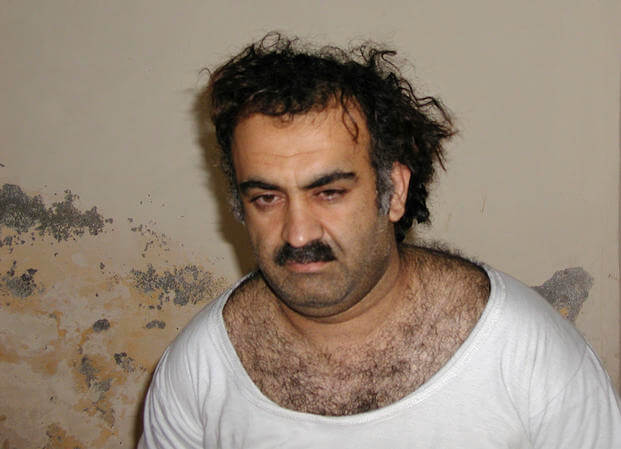
WASHINGTON — Khalid Sheikh Mohammed, accused as the mastermind of al-Qaida’s Sept. 11, 2001, attacks[1] on the United States, has agreed to plead guilty, the Defense Department said Wednesday. The development points to a long-delayed resolution in an attack that killed thousands and altered the course of the United States and much of the Middle East.
Mohammed and two accomplices, Walid Bin Attash and Mustafa al-Hawsawi, are expected to enter the pleas at the military commission at Guantanamo Bay, Cuba, as soon as next week.
Terry Strada, the head of one group of families of the nearly 3,000 direct victims of the 9/11 attacks, invoked the dozens of relatives who have died while awaiting justice for the killings when she heard news of the plea agreement.
“They were cowards when they planned the attack," she said of the defendants. "And they’re cowards today."
Pentagon officials declined to immediately release the terms of the plea bargain. The New York Times, citing unidentified Pentagon officials, said the terms included the men’s longstanding condition that they be spared risk of the death penalty.
The U.S. agreement with the men comes more than 16 years after their prosecution began for al-Qaida's attack. It comes more than 20 years after militants commandeered commercial airliners to use as fuel-filled missiles, flying them into the World Trade Center in New York and the Pentagon.
Al-Qaida hijackers headed a fourth plane to Washington, but crew members and passengers tried to storm the cockpit, and the plane crashed into a Pennsylvania field.
The attack triggered what President George W. Bush's administration called its war on terror, prompting the U.S. military invasions of Afghanistan and Iraq and years of U.S. operations against armed extremist groups elsewhere in the Middle East.
The attack and U.S. retaliation brought the overthrow of two governments outright, devastated civilian communities and countries caught in the battle, and played a role in inspiring the 2011 Arab Spring popular uprisings against authoritarian Middle East governments.
At home, the attacks inspired a sharply more militaristic and nationalist turn to American society and culture.
U.S. authorities point to Mohammed as the source of the idea to use planes as weapons. He allegedly received approval from al-Qaida leader Osama bin Laden, whom U.S. forces killed in 2011, to craft what became the 9/11 hijackings and killings.
Authorities captured Mohammed in 2003. Mohammed was subjected to waterboarding 183 times while in CIA custody before coming to Guantanamo, and targeted by other forms of torture and coercive questioning.
The use of torture has proven one of the most formidable obstacles in U.S. efforts to try the men in the military commission at Guantanamo, owing to the inadmissibility of evidence linked to abuse.
Daphne Eviatar, a director at the Amnesty International USA rights group, said Wednesday she welcomed news of some accountability in the attacks.
She urged the Biden administration to close the Guantanamo Bay detention center, which holds people taken into custody in the so-called war on terror. Many have since been cleared, but are awaiting approval to leave for other countries.
Additionally, Eviatar said, “the Biden administration must also take all necessary measures to ensure that a program of state-sanctioned enforced disappearance, torture and other ill-treatment will never be perpetrated by the United States again."
Strada, national chairperson of a group of families of victims called 9/11 Families United, had been at Manhattan federal court for a hearing on one of many civil lawsuits when she heard news of the plea agreement.
Strada said many families have just wanted to see the men admit guilt.
“For me personally, I wanted to see a trial,” she said. “And they just took away the justice I was expecting, a trial and the punishment.”
© Copyright 2024 Associated Press. All rights reserved. This material may not be published, broadcast, rewritten or redistributed.